什么是Fiber双缓存
React在内存中会构建两个Fiber树,当前显示的画面对应的是current Fiber树,React内部会根据Update对状态进行计算(计算过程暂不清楚),并构建一个新的workInProgress Fiber树。构建完成后将FiberRoot的current指针指向workInProgress的RootFiber节点,浏览器按照新的Fiber树进行渲染,两个Fiber树就完成了一次切换。
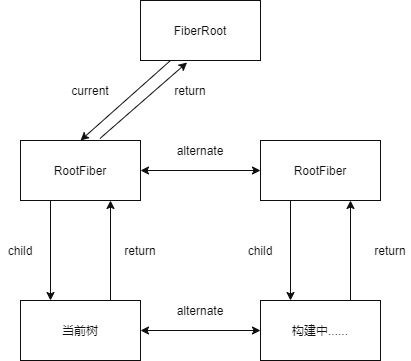
mount阶段fiber双缓存的构建过程
该过程发生在FiberRoot和RootFiber构建之后,此时Fiber树的关系如图。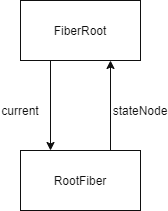
performSyncWorkOnRoot
初次调用时由于workInProgress还没有构建,因此直接调用lanes = getNextLanes(root, NoLanes); 该函数根据传入的FiberRoot生成新的lanes(与组件更新优先级相关的变量)。
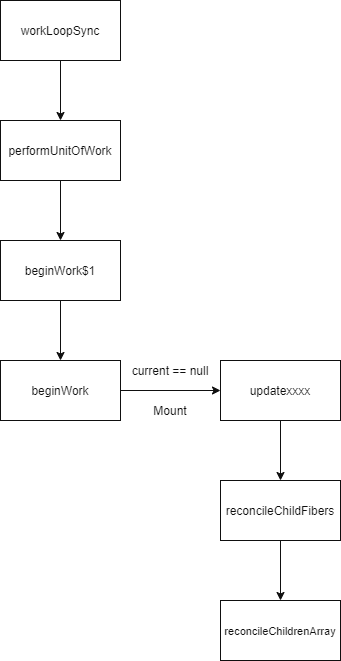
workLoopSync
下面看一下源码
function workLoopSync() {
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}只要workInProgress不是null,该函数就会连续调用performUnitOfWork
performUnitOfWork
该函数的参数时workInProgress的RootFiber,该函数内部调用beginWork$1
beginWork
由于该函数第一次调用传入的是RootFiber,因此跳转到传入div节点时分析该过程,此时current是null,因此进入mount过程了。
else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
} didReceiveUpdate用于标识Fiber是否需要更新,因为是mount,所以设置为false
将传入节点(div)的Lanes设置为NoLanes(与更新优先级相关的变量)
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;下面根据workInProgress的tag进入不同的构建过程。
case HostComponent:
return updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);updateHostComponent
该函数内部调用reconcileChildren将jsx对象构建成为fiber,并返回workInProgress.child
reconcileChildren
先不关注updateHostComponent,下面看一下reconcileChildren的源码
function reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderLanes) {
if (current === null) {
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(workInProgress, null, nextChildren, renderLanes);
} else {
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(workInProgress, current.child, nextChildren, renderLanes);
}
}该函数接受四个参数,此时四个参数分别为null,div节点,数组(数组内包含的子元素,此时有两个jsx对象,一个文本对象),renderlanes优先级。由于current是null,将当前对象的child指针指向子节点
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(workInProgress, null, nextChildren, renderLanes);mountChildFibers实际上是childReconciler的返回值,调用childReconciler返回的是函数reconcileChildFilbers
var mountChildFibers = ChildReconciler(false);这段代码的调用实际上是
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(workInProgress, null, nextChildren, renderLanes);reconcileChildFibers
函数内部根据传入newChild的类型选择创建新fiber的方式,此时newChild是一个包含文本对象和jsx对象的数组,因此调用
if (isArray$1(newChild)) {
return reconcileChildrenArray(returnFiber, currentFirstChild, newChild, lanes);
}reconcileChildrenArray
该函数内比较重要的部分如下
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
var _newFiber = createChild(returnFiber, newChildren[newIdx], lanes);
if (_newFiber === null) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(_newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = _newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = _newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = _newFiber;
}该过程是对child数组的一次便利,首先调用createChild生成一个fiber,因为目前构建的是children的第一个元素,因此previousNewFiber == null,如果不是第一次构建,则将sibling指针指向其他的
兄弟元素,最终返回第一个子节点resultingFirstChild
从当前来看reconcileChildren大概有两个功能
- 构建子节点之间的兄弟关系,即sibling指向
- 获取第一个子节点作为父节点的child并返回
到此为止第一个子节点的构建过程基本结束,后续还有一些收尾工作(暂时不关注),第二个节点的构建依然是类似的过程,在workLoopSync中循环调用performUnitOfWork直到所有节点构建结束。
summary