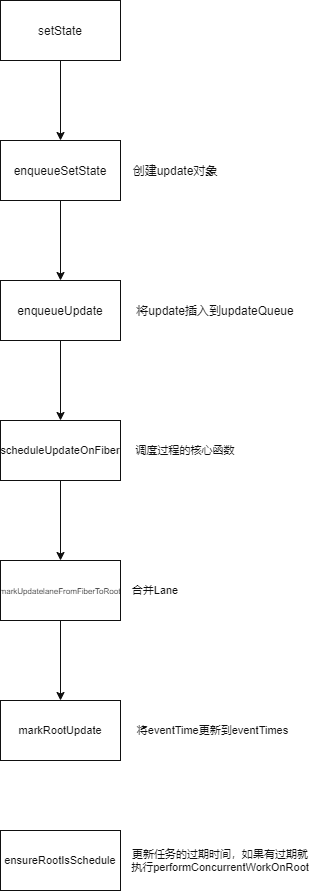
很简单的demo,一个button而已,看一下setState过程发生了啥
export default class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {value: 0}
}
handler(){
this.setState({value: this.state.value + 1})
}
render(){
return(
<div className='app'>
<button onClick={() =>{this.handler()}}>{this.state.value}</button>
</div>
)
}
}setState -> enqueueSetState
Component.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) {
if (!(typeof partialState === 'object' || typeof partialState === 'function' || partialState == null)) {
{
throw Error( "setState(...): takes an object of state variables to update or a function which returns an object of state variables." );
}
}
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, 'setState');
};这个setState就是component内调用的setState,partialState就是新传入的state({value: 1})。
后面调用enqueueSetState,this就是触发更新的App component
看一下enqueueSetState
function (inst, payload, callback) {
var fiber = get(inst);
var eventTime = requestEventTime();
var lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
var update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
{
warnOnInvalidCallback(callback, 'setState');
}
update.callback = callback;
}
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}解释一下这几个参数:
- inst(instance), 传入的App component
- payload,传入的state对象{value: 1}
var eventTime = requestEventTime();
var lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);eventTime和react的任务调度相关,事件发生的事件。lane和优先级相关。
调用createUpdate创建一个update对象
function createUpdate(eventTime, lane) {
var update = {
eventTime: eventTime,
lane: lane,
tag: UpdateState,
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null
};
return update;
}update对象包含该update的发生事件(eventTime),优先级(lane)等,payload就是新的state,该函数调用结束后手动更新,update之间通过next连接成链表。
enqueueUpdate
fiber上的update是一个环状链表,enqueueUpdate将创建的update插入到该链表中。
fiber上的updateQueue类似这样(如果fiber还没有mount,则updateQueue === null)
{
baseState: {value: 0}
effects: null
firstBaseUpdate: null
lastBaseUpdate: null
shared: {pending: null}
}下面插入update
if (pending === null) {
update.next = update;
} else {
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}如果没有其他update,则新的update自己成环。如果之前有update则将new update插入到上一个创建的update后面构成环。
sharedQueue.pending = update;将pending指向新的update
scheduleUpdateOnFiber
这个函数用于调度update
markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot
markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot的代码比较长,贴一下关键的部分
下面是合并lane的部分
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);
//合并new update的lane和fiber自身的lane
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, lane);
//合并同一层的fiber的lane
while (parent !== null) {
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);
alternate = parent.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.childLanes = mergeLanes(alternate.childLanes, lane);
} else {
{
if ((parent.flags & (Placement | Hydrating)) !== NoFlags) {
warnAboutUpdateOnNotYetMountedFiberInDEV(sourceFiber);
}
}
}
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
// 将新的lane不断合并到parend.childLanes上,别忘了同层的fiber也要合并总结一下合并lane的过程:
- 合并新的lane和fiber.lanes
- 合并同层fiber(alternate)的lane
- 将lane和每一个parent.childLanes合并
markRootUpdate
主要用于将eventTime放入到eventTimes数组内
root.pendingLanes |= updateLane首先将update.lane合并到root.pendingLanes,也就是说root.pendingLanes保存的是新的update.lane
var eventTimes = root.eventTimes;对于一个lanes,存在eventTimes表示每一位的过期时间(如果lane的第i位为1,则eventTimes[i] != -1)。
var index = laneToIndex(updateLane);
function pickArbitraryLaneIndex(lanes) {
return 31 - clz32(lanes);
}
eventTimes[index] = eventTime;这一段就是将eventTime赋值到eventTimes[i]上。laneToIndex内部调用了pickArbitraryLaneIndex,clz32获取lanes转换为无符号二进制数前面0的个数,换句话说index就是二进制lane中左侧第一个1的位置。接下来就是eventTimes[index] = eventTime
总结一下就是按照lane中1的位置,将eventTime更新到eventTimes数组上。markRootUpdate就是更新每个update的过期时间。
回到scheduleUpdateOnFiber
if (lane === SyncLane) {
// some code
} else {
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
schedulePendingInteractions(root, lane);
if (executionContext === NoContext) {
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbackQueue();
}
}
} 用sync模式启动,因此进入lane===SyncLane的逻辑,看一下ensureRootIsScheduled
ensureRootIsScheduled -> markStarvedLanesAsExpired
这个函数将新建update的过期时间更新到expirationTimes上。
while (lanes > 0) {
var index = pickArbitraryLaneIndex(lanes);
var lane = 1 << index;
var expirationTime = expirationTimes[index];
if (expirationTime === NoTimestamp) {
if ((lane & suspendedLanes) === NoLanes || (lane & pingedLanes) !== NoLanes) {
expirationTimes[index] = computeExpirationTime(lane, currentTime);
}
} else if (expirationTime <= currentTime) {
root.expiredLanes |= lane;
}
lanes &= ~lane;
}这一部分比较重要,首先就像markRootUpdate一样计算lanes(pendingLanes,还未被计算)左侧1的位置,然后检测一下expirationTimes在该位置的值,-1表示没有任务,其他值表示过期时间。
if (expirationTime === NoTimestamp) {
if ((lane & suspendedLanes) === NoLanes || (lane & pingedLanes) !== NoLanes) {
expirationTimes[index] = computeExpirationTime(lane, currentTime);
}
} else if (expirationTime <= currentTime) {
root.expiredLanes |= lane;
}这里计算出过期时间后将其赋值给expiredTimes,后面就是每次发现任务过期就执行 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,具体调度过程下一次详细写一下。
summary