demo
export default function App(){
let [val, setVal] = useState(0)
useEffect(() => console.log(val), val)
function click(){
setVal(val + 1)
}
return(
<div className='app'>
<button onClick={() => { click() }}>{val}</button>
</div>
)
}mount时的useEffect
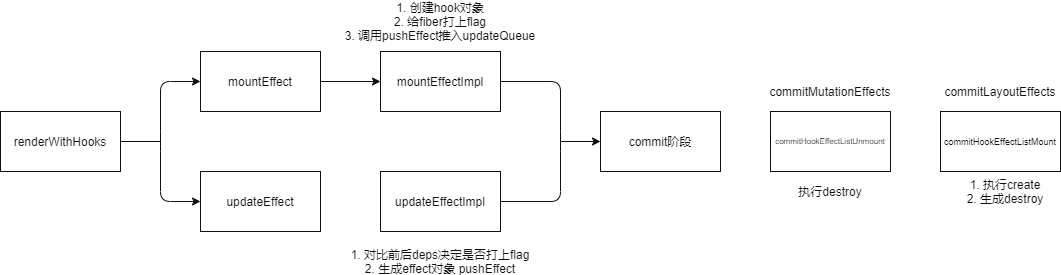
首先看一下mount时的调用栈
mountIndeterminateComponent在函数组件首次渲染时调用,主要作用就是启动renderWithHooks,在renderWithHooks内直接调用函数组件,返回children
调用方式如下
var children = Component(props, secondArg)就像普通的函数一样,在App()内调用dispatcher.useEffect,dispatcher时包含了所有hook的一个对象,根据当前阶段不同,包含的成员也不同,mount阶段实际上调用的是dispatcher.mountEffect
mountEffect -> mountEffectImpl
先看一下mountEffect
function mountEffect(create, deps) {
{
// some code
}
return mountEffectImpl(Update | Passive, Passive$1, create, deps);
}mountEffect接受的两个参数就是我们穿的callback和依赖值
create -> callbak
deps -> 第二个参数, 依赖值
看一下mountEffectImple
function mountEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
var hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
var nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(HasEffect | hookFlags, create, undefined, nextDeps);
}mountWorkInProgressHook作用比较简单,创建一个hook对象,然后把hook挂到fiber.mimoizedState上,简单看一下
function mountWorkInProgressHook() {
var hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}hook之间通过next连接
后面这个pushEffect比较重要,仔细看一下
function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
var effect = {
tag: tag,
create: create,
destroy: destroy,
deps: deps,
next: null
};
var componentUpdateQueue = currentlyRenderingFiber$1.updateQueue;
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) {
componentUpdateQueue = createFunctionComponentUpdateQueue();
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue;
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
var lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
if (lastEffect === null) {
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
var firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
lastEffect.next = effect;
effect.next = firstEffect;
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
}
}
return effect;
}这四个参数里面,create就是调用useEffect的第一个参数callback,destory是callback调用后的返回值
首先创建一个effect对象,包含create,destory等参数
var effect = {
tag: tag,
create: create,
destroy: destroy,
deps: deps,
next: null
};后面这个if else就是把effect对象挂载到fiber.updateQueue上,用于后面更新。
总结一下useEffectImpl的作用:
- 创建hook对象,挂到fiber.mimoizedState上
- 给fiber打上flag,标明effectHook存在
- 创建effect对象(包含create,destory),把effect添加到updateQueue上
到这里useEffect在beginWork里的工作基本就结束了,useEffect的callback是在视图更新后调用的,所以useEffect的调用过程要在commit阶段才能看到
commitHookEffectListUnmount
这个函数的作用主要是执行useEffect的destory函数,执行阶段实在commit阶段 -> commitRootImpl -> commitMutationEffects(也就是commit阶段的第二个子阶段)
function commitHookEffectListUnmount(tag, finishedWork) {
var updateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue;
var lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
var firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
var effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & tag) === tag) {
var destroy = effect.destroy;
effect.destroy = undefined;
if (destroy !== undefined) {
destroy();
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}其实逻辑比较简单,获取完整的effectList环状链表,然后通过while循环不断获取effect(这里要确认tag由useEffect产生),然后检测是否有destroy(destroy源自create),如果有就执行destory
commitHookEffectListMount
function commitHookEffectListMount(tag, finishedWork) {
var updateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue;
var lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
var firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
var effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & tag) === tag) {
var create = effect.create;
effect.destroy = create();
{
var destroy = effect.destroy;
if (destroy !== undefined && typeof destroy !== 'function') {
// some code
}
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}到这就可以知道,为什么destory先于create执行,commitHookEffectListMount在commit的第三个阶段(commitLayoutEffects)执行。这里也是遍历effectList,然后获取create并执行,create执行后的返回值就是destory。
最后的问题,useEffect如何感知deps的变化?
这里要回到Function Component渲染的入口函数 renderWithHook, 在renderWithHook内调用hook相关函数,前面提到过,根据阶段不同,dispatcher包含的hook函数不同,在update阶段这里调用dispatcher.updateEffect(mount阶段是mountEffect)。
function updateEffectImpl(fiberFlags, hookFlags, create, deps) {
var hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
var nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
var destroy = undefined;
if (currentHook !== null) {
var prevEffect = currentHook.memoizedState;
destroy = prevEffect.destroy;
if (nextDeps !== null) {
var prevDeps = prevEffect.deps;
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
pushEffect(hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
return;
}
}
}
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.flags |= fiberFlags;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(HasEffect | hookFlags, create, destroy, nextDeps);
}主要关注中间if的部分,对比旧的effect(currentHook.memoizedState)和新传入的参数,对比过程在areHookInputsEqual内,看一下areHookInputsEqual
function areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps) {
{
if (ignorePreviousDependencies) {
// Only true when this component is being hot reloaded.
return false;
}
}
if (prevDeps === null) {
{
// some code
}
return false;
}
{
if (nextDeps.length !== prevDeps.length) {
// some code
}
}
for (var i = 0; i < prevDeps.length && i < nextDeps.length; i++) {
if (objectIs(nextDeps[i], prevDeps[i])) {
continue;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}就是通过for遍历new array和old array对比一下是否有变化,不相等就返回false
总结一下,在update阶段的renderWithHook内,对比new deps和old deps,如果没有变化就pushEffect然后return,如果有变化就要给fiber打上相应的flag,用户commit阶段更新。
summary