简单说一下AES加密CBC模式的工作原理,首先AES加密会涉及几个基本概念:
- 原始数据
- 加密key(key的长度有特定要求,只能是16/24/32 byte)
- 偏移
CBC模式将原始数据均分为若干块,从第一块开始使用key进行加密,然后第二原始块与第一个加密块进行XOR运算后再次用key加密,以此类推即可。
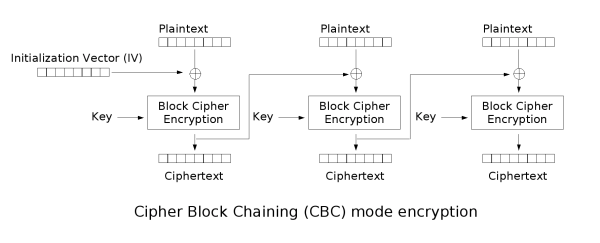
环境准备
前端主要用crypto-js和axios
npm i crypto-js --save
npm i axios-js --save后端用gin,crypto
get get github.com/gin-contrib/cors
get get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
get get golang.org/x/crypto前端加密
这里我们选用16 byte的key进行加密
function aesCbcEncrypt(text) {
const key = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("0".repeat(16))
let encrypted = aes.encrypt(text, key, {mode: CryptoJS.mode.CBC, padding: CryptoJS.pad.Pkcs7, iv: key})
return encrypted.ciphertext.toString(CryptoJS.enc.Hex);
}aes.encrypt对key的类型是有要求的(string | WordArray),使用Utf8.parse解决编码的问题,同时得到一个utf8的WordArray
然后调用aes.encrypt进行加密,解释一下padding的作用:
前面提到CBC加密时会把数据均分为若干个块,但是如果原始数据的长度不能均分就需要填充 ,主流的填充方式有Pkcs7和Pkcs5,在AES加密中这两种方式没有区别,这里以Pkcs7为例,经过Pkcs7填充的数据最后一位代表填充的位数,在解密时进行upadding即可
返回的字符串用hex处理,防止编码出现问题,因此解密时需要先用hex decode
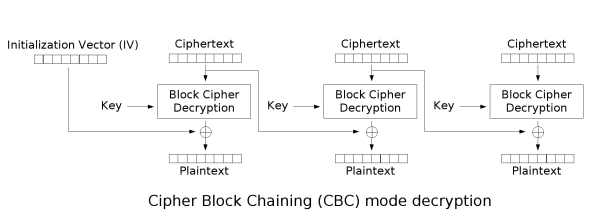
后端解密
首先时upadding的实现,之前提到了最后一位代表填充的位数,这里获取最后一位的数值即可
func PKCS7UnPadding(plantText []byte) []byte {
length := len(plantText)
unpadding := int(plantText[length-1])
return plantText[:(length - unpadding)]
}核心解密函数的实现(解密前记得调用hex.DecodeString)
func AesCBCDecrypt(encrypted []byte) (decrypted []byte) {
key := []byte(strings.Repeat("0", 16))
block, err := aes.NewCipher(key)
if err != nil {
log.Print("create newCipher error")
}
blockModel := cipher.NewCBCDecrypter(block, key)
plantText := make([]byte, len(encrypted))
blockModel.CryptBlocks(plantText, encrypted)
plantText = PKCS7UnPadding(plantText)
return plantText
}aes.NewCipher创建一个cipher用于后续解密,这里传入key决定解密算法的位数,然后使用cipher创建一个用于CBC解密的专用对象(cipher.NewCBCDecrypter),最后调用CryptBlocks解密就可以了,解密后的数据用Pkcs7UnPadding去除填充部分得到的就是原始数据。
总结一下解密过程

